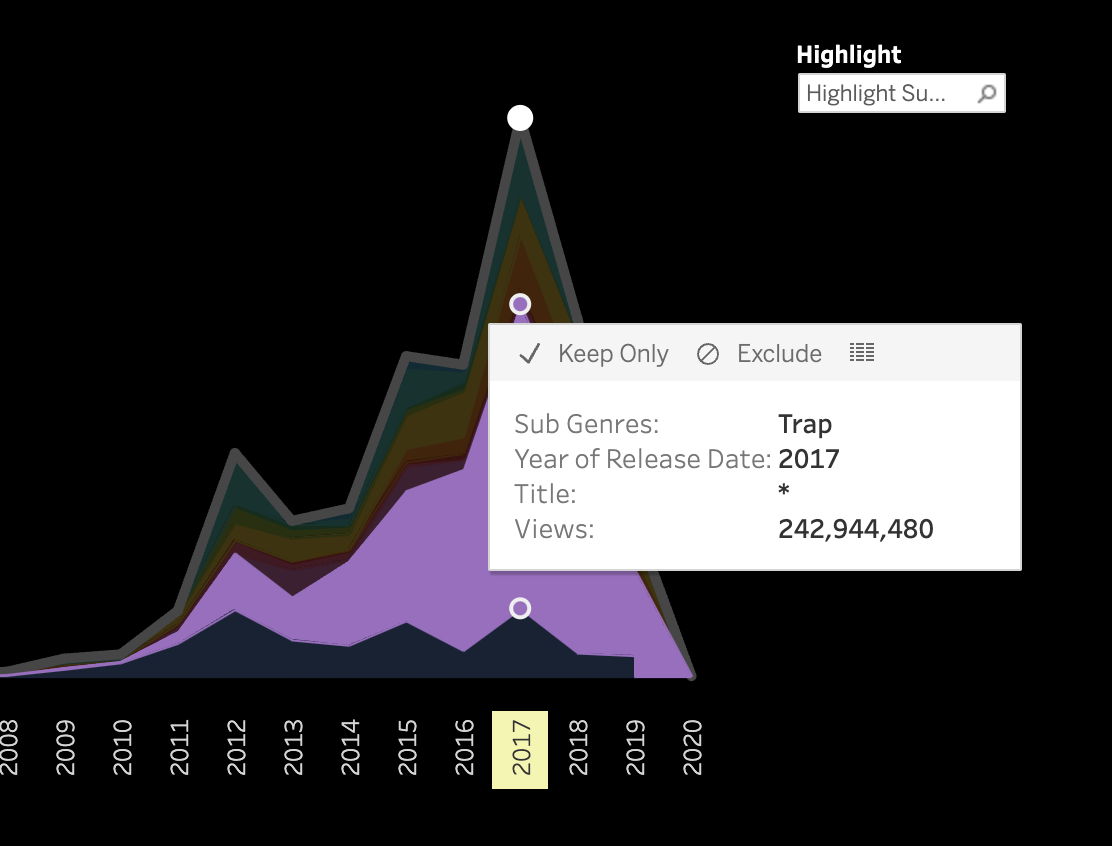
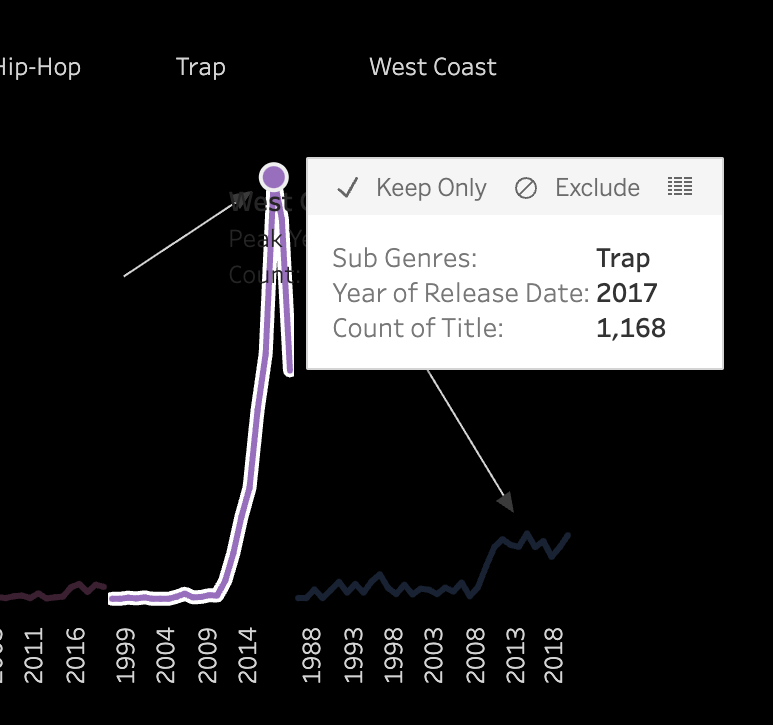
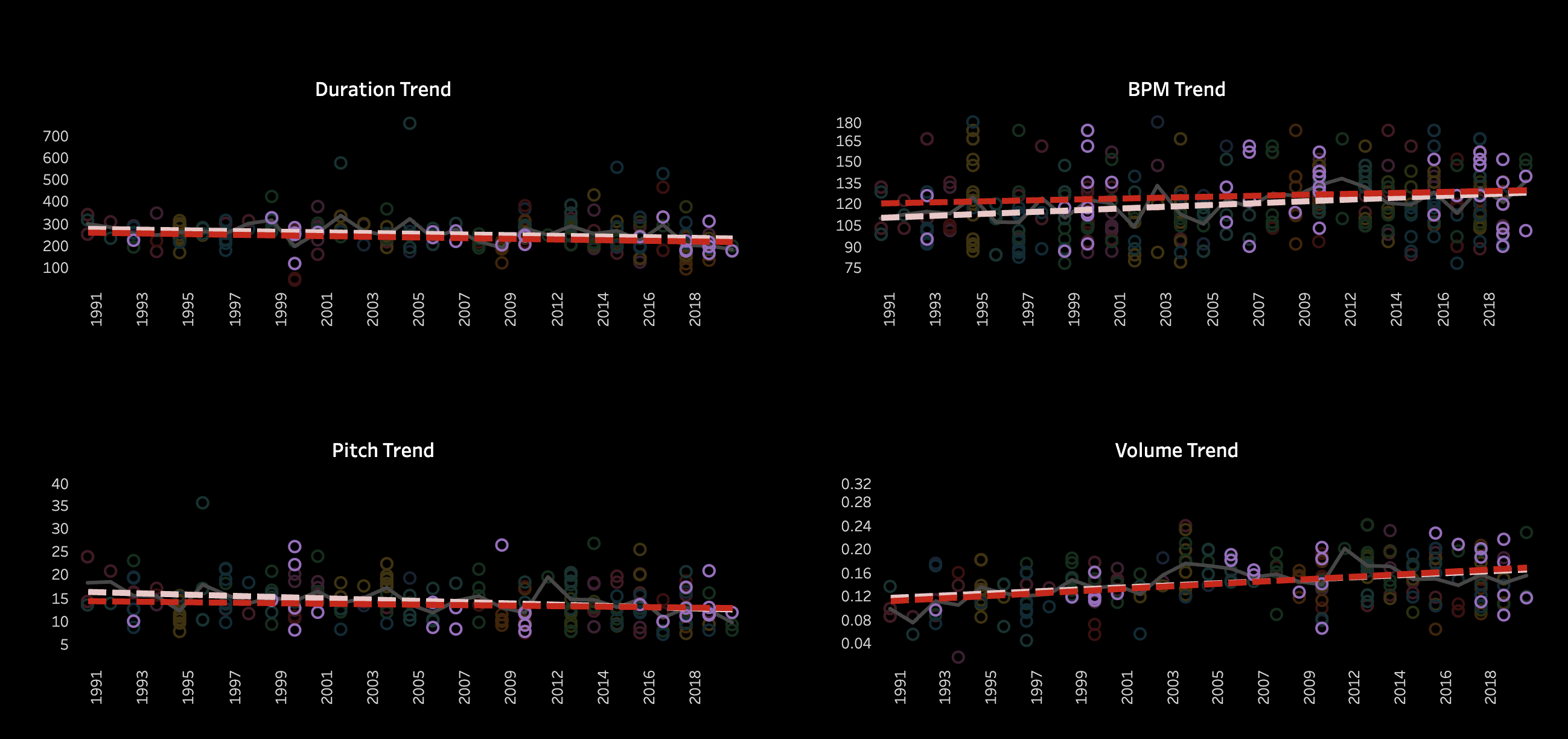
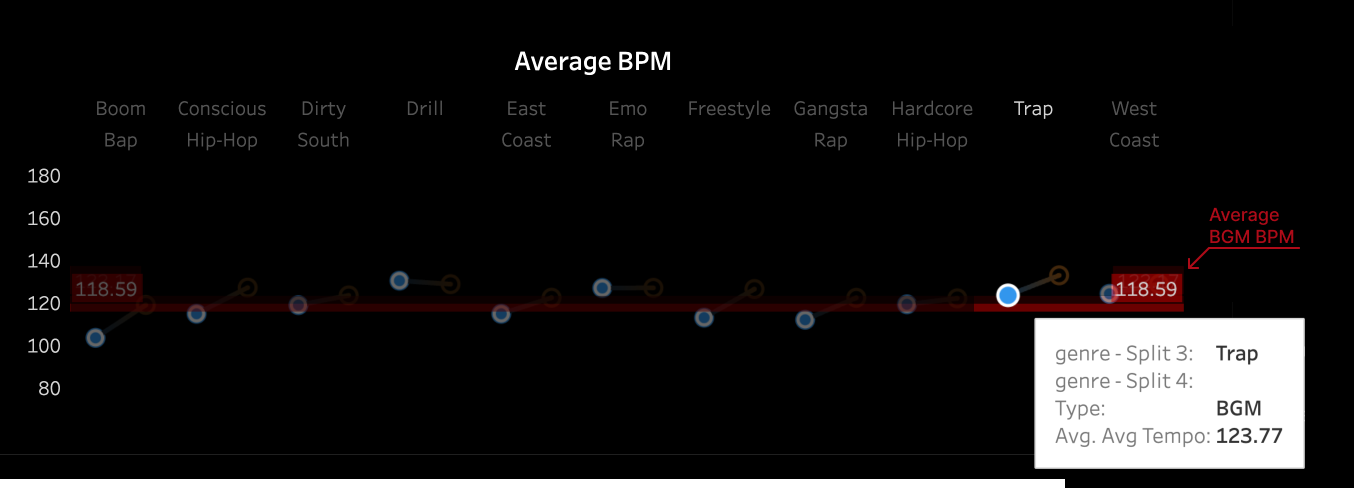
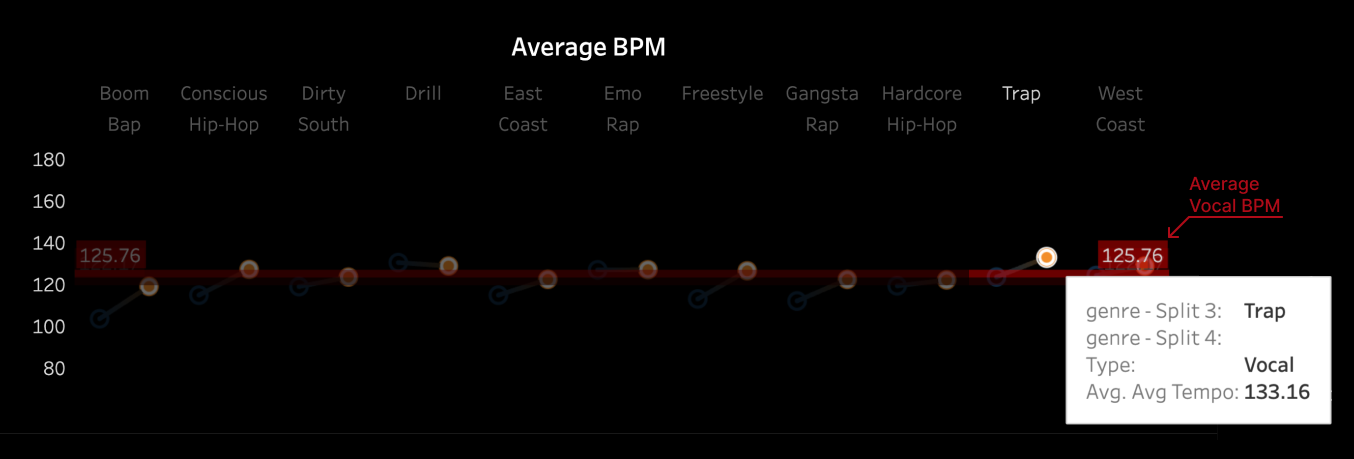
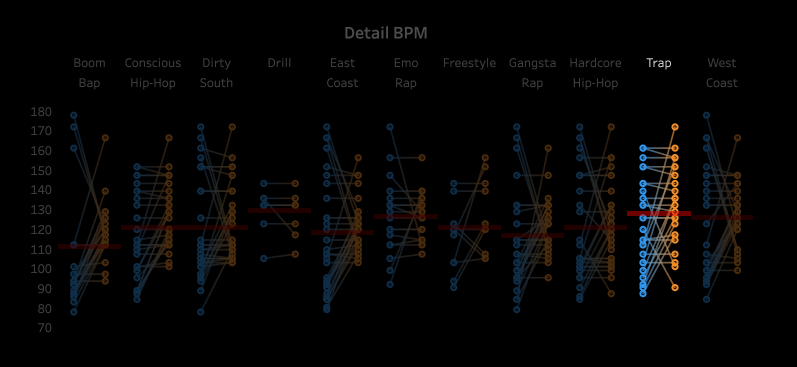
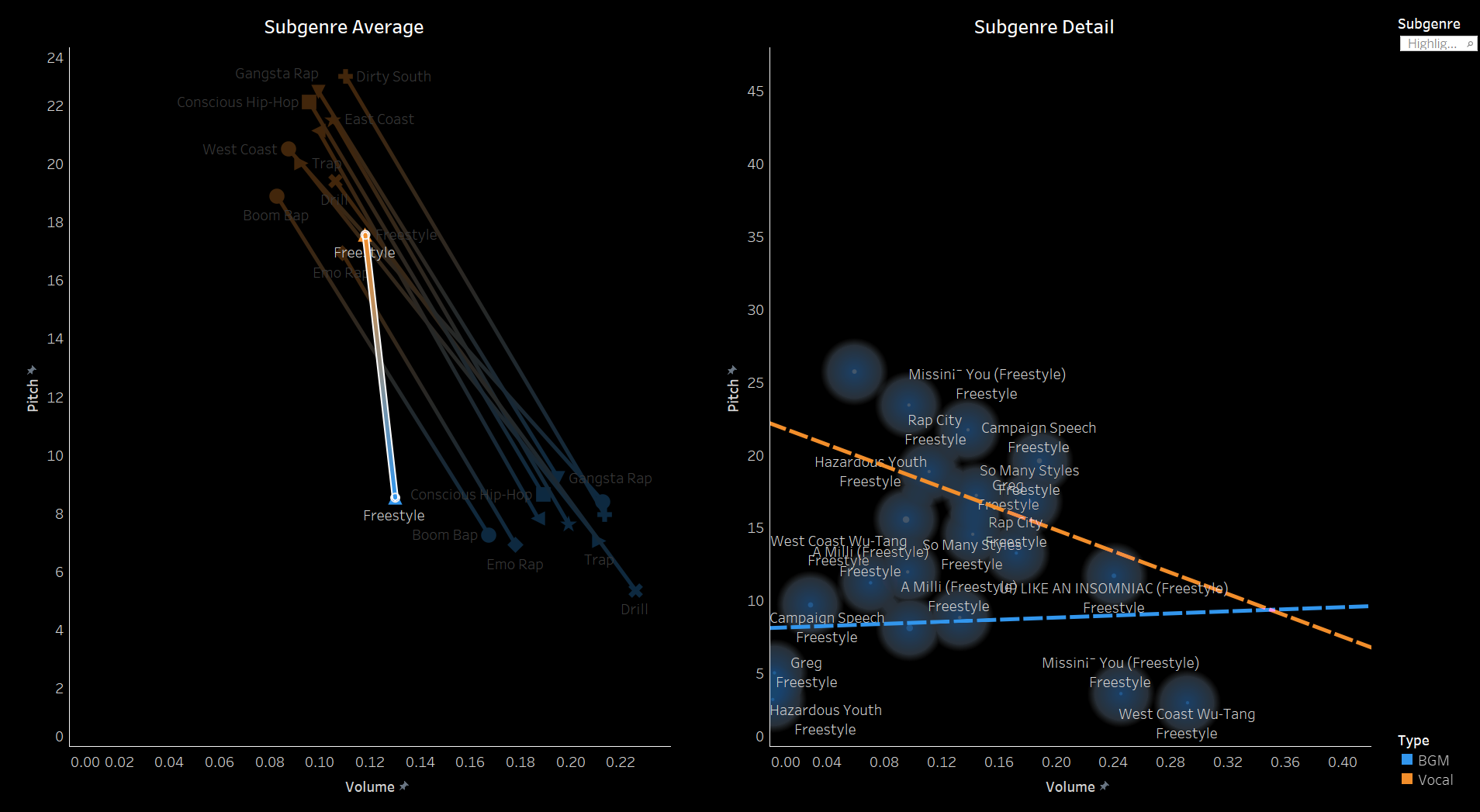
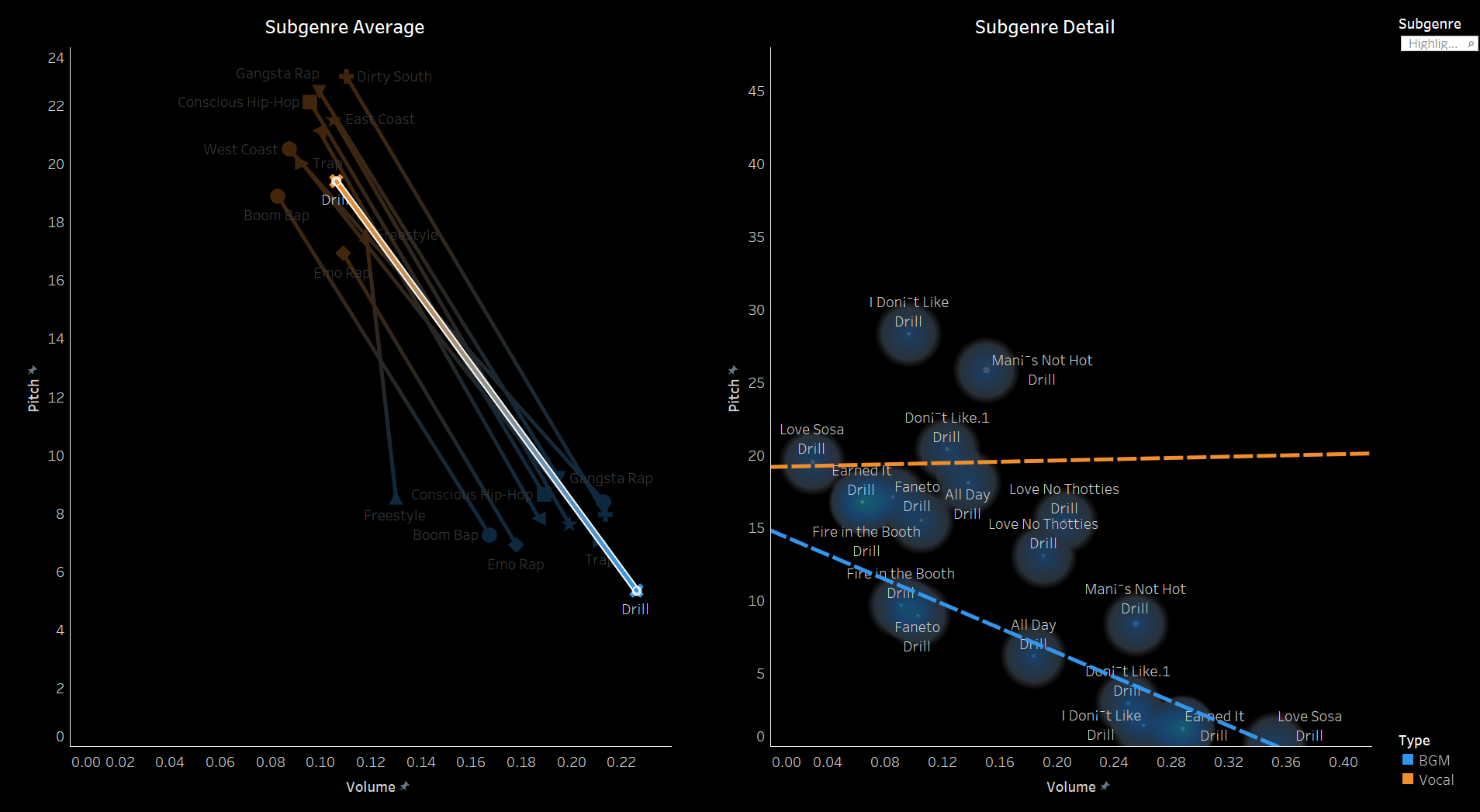
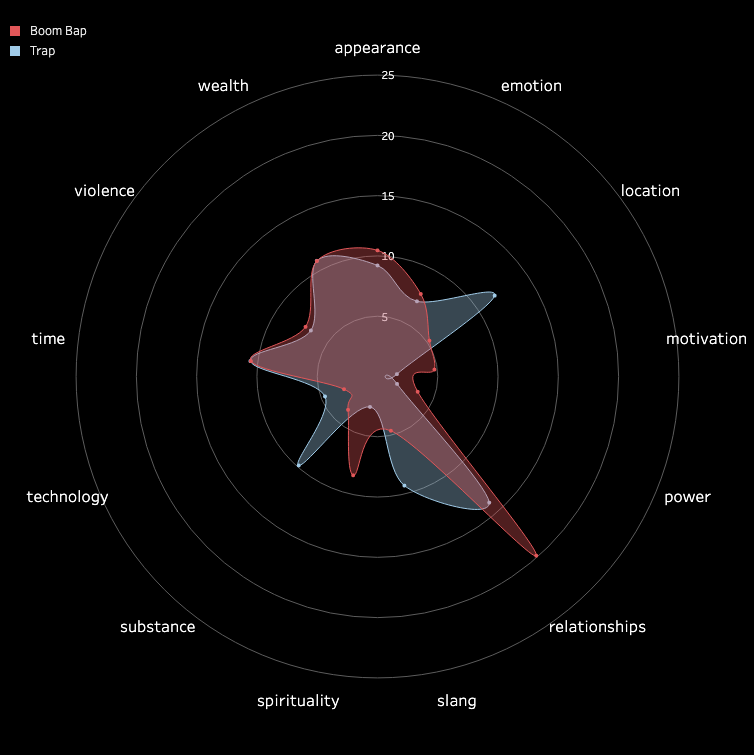
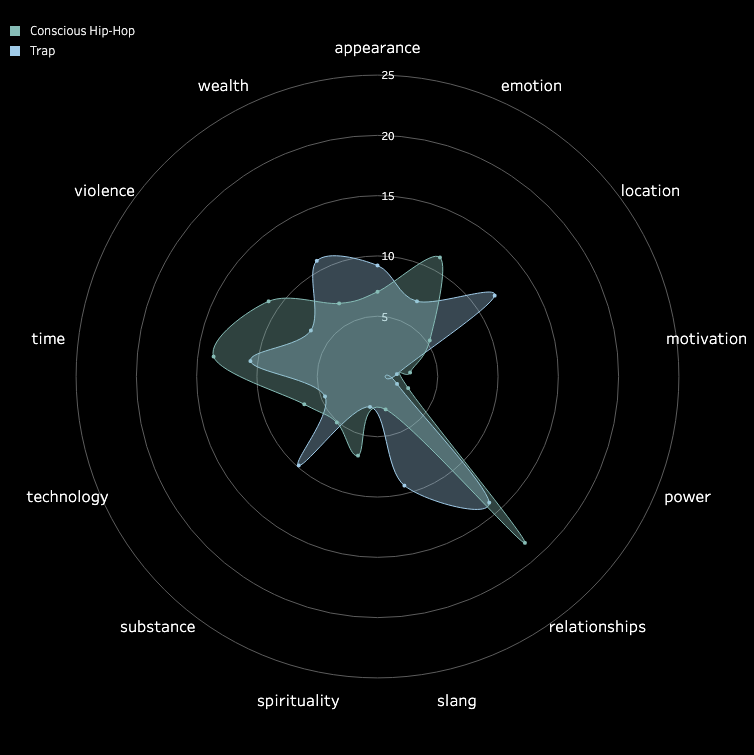
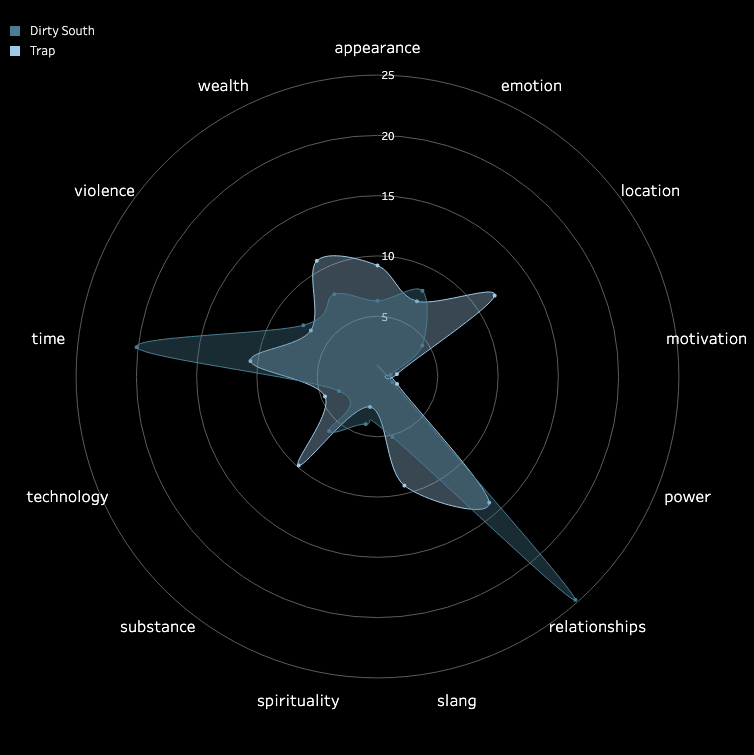
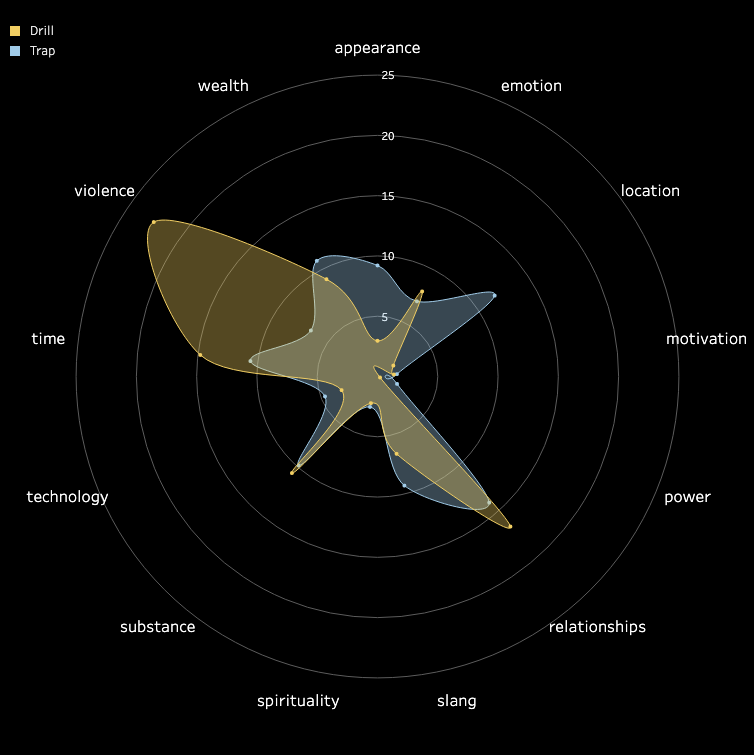
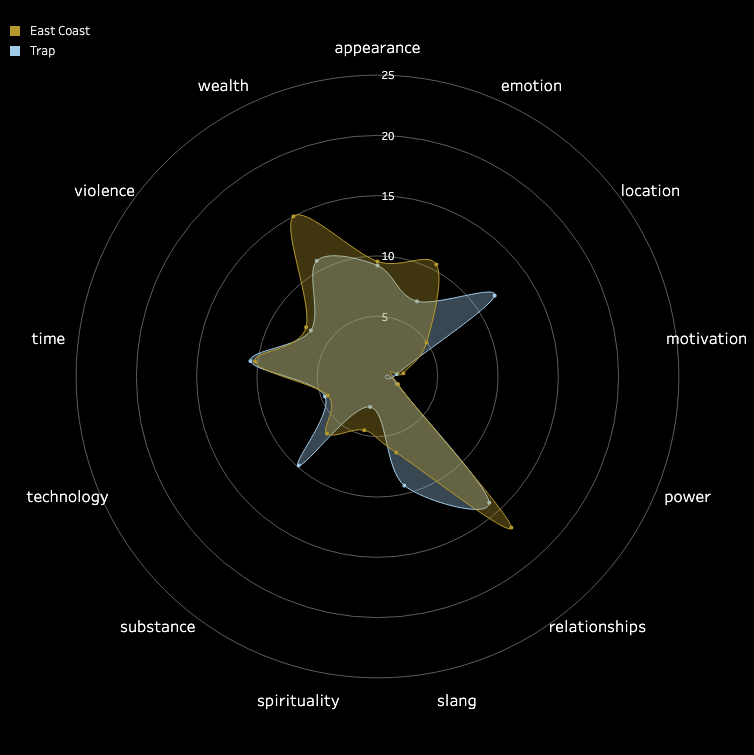
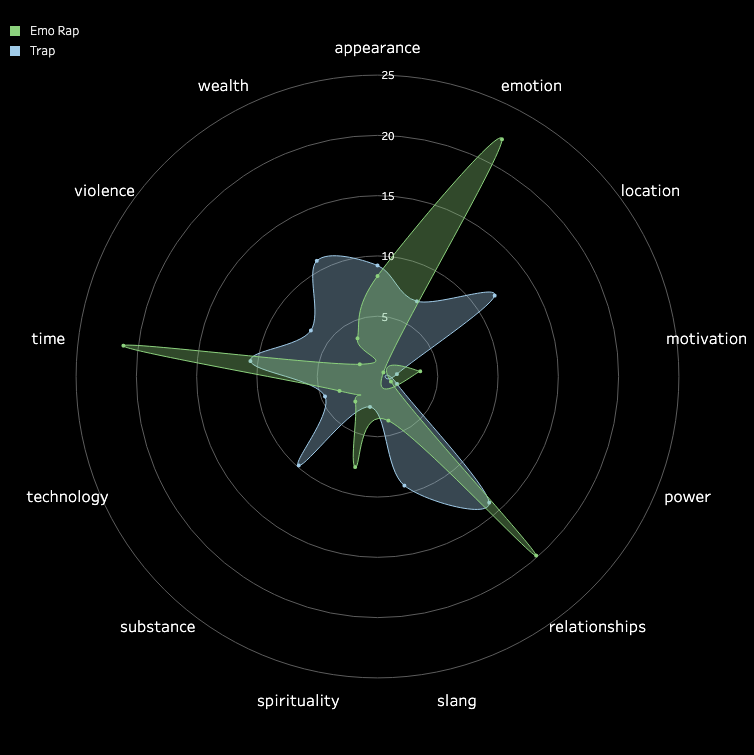
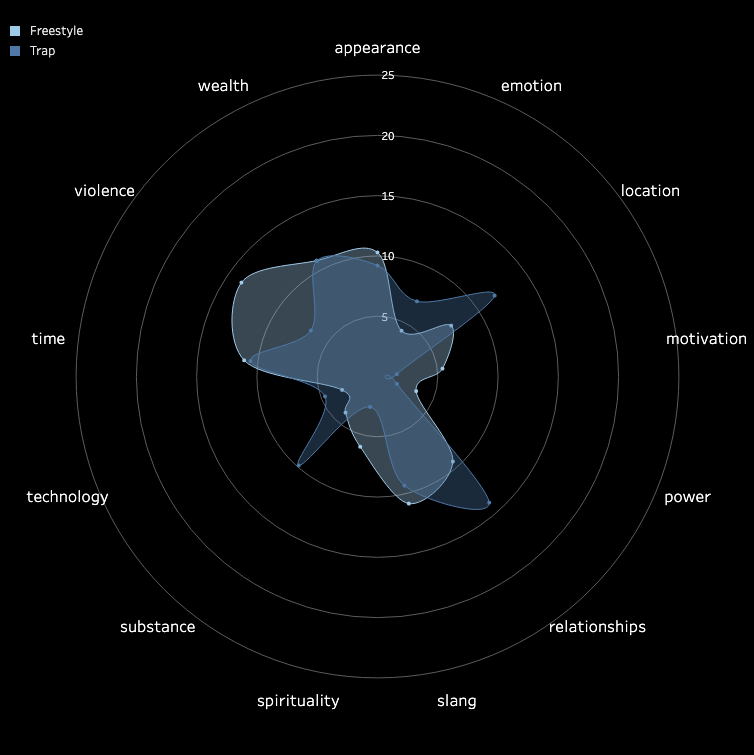
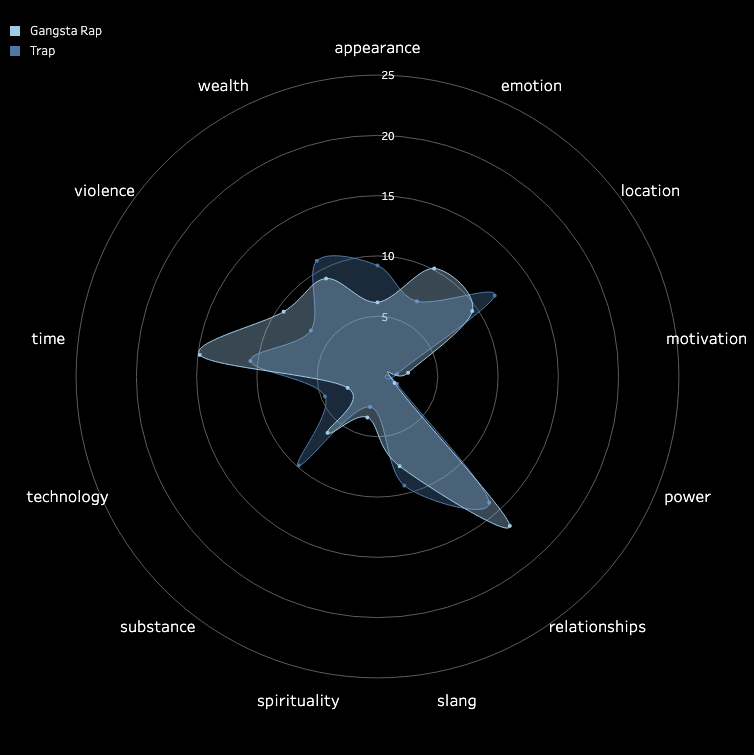
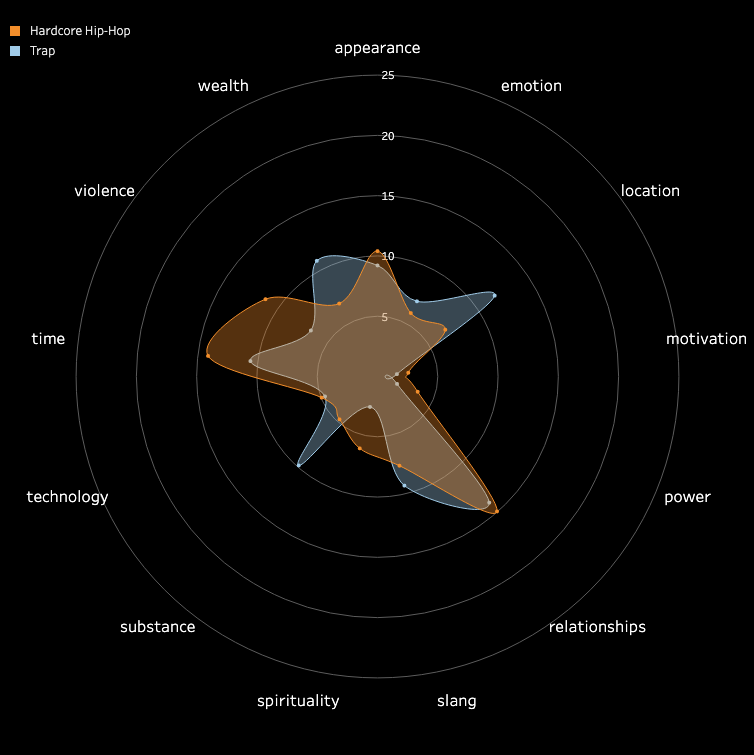
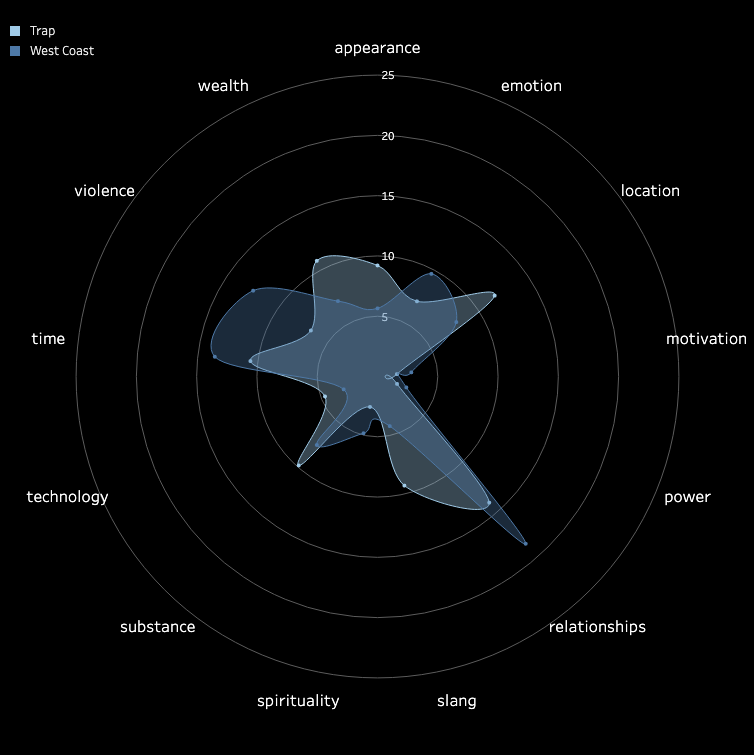
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.
3.2 Pitch and Volume
We conducted a frame-by-frame analysis of pitch and volume for the top 10 songs in each
subgenre,
visualizing each song on a pixel display with the horizontal axis representing time.
Each song features two tracks: the upper track for BGM and the lower track for vocals.
Similarities Among Top Songs: There are notable similarities among the top songs,
particularly in their BGM. These include periodic high-frequency pitches and a generally
fast tempo with higher volume levels. In contrast, vocals tend to dominate the higher
frequencies but exhibit relatively lower volumes. While further insights could be drawn from
direct comparisons between specific songs, we do not delve deeper here.
Differences in Time-Frequency Characteristics Across Subgenres:
In addition to similarities, distinct differences in time-frequency characteristics can be
observed across subgenres. For instance, the frequency of high-pitched sounds in the BGM of
Boom Amp is significantly lower compared to Trap. This highlights Trap as a genre
characterized by faster tempos and more frequent intermittent high-frequency sounds,
distinguishing it from other subgenres.